Details
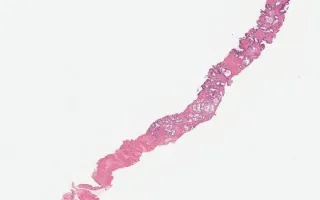
Prostate biopsy.
Prostate adenocarcinoma is a common malignancy in men and incidence increases with age. Major criteria for prostate adenocarcinoma include infiltrative architecture with increased density of small circular glands, loss of basal cell layer, and cytologic abnormalities including nuclear enlargement and prominent nucleoli. Minor criteria include nuclear hyperchromasia, wispy blue mucin, pink amorphous secretions, intraluminal crystalloids, amphophilic cytoplasm, adjacent high grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia and mitoses.
Foamy gland variant is a relatively common variant of prostate adenocarcinoma. It is seen in 20% of carcinomas but is mostly admixed with the typical acinar adenocarcinoma. It is characterized by abundant foamy cytoplasm. It may vary from well-formed glands to fused or ill-formed glands. Nuclear abnormalities are not always seen, as they may be small and pyknotic. Benign mimickers include Copwer gland and mucinous metaplasia. Infiltrative architecture may alert the diagnostician to consider immunohistochemical stains to confirm loss of basal cell layer.
This slide shows H&E stain. See Related Content for 34BE stain.