Details
Child with a reddish-brown nodule on his upper back.
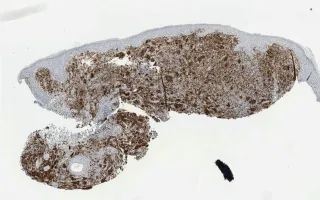
Juvenile xanthogranuloma is a non-Langerhans cell histiocytic and dendritic cell proliferation that is common in young children. 75% of cases are diagnosed before one year of age. Common sites include the skin, soft tissue - including skeletal muscle - and rarely the cranial cavity. The histological findings include: (1) sheets of mononuclear histiocytes accompanied by multi-nucleated giant cells, including Touton cells with a peripheral wreath of nuclei (seen here); (2) vacuolated xanthomatized cells; and (3) an inflammatory infiltrate of eosinophils and lymphocytes. The CD68 stain demonstrates the histiocytic origin of the proliferation. They are usually also Factor 13A positive, S100 positive (variable) and CD1a negative.
This slide shows CD68 stain. See Related Content for H&E stain.